What is DMR?
DMR, which stands for Digital Mobile Radio, is a prominent acronym in the field of digital communication. Reliable and transparent communication is essential in today’s world of expanding connectivity, regardless of the industry. Effective information interchange is essential for smooth operations and prompt reactions, for both businesses and public safety workers, or for the non-commercial communities. This is where DMR technology providing dependable two-way radio communication with a number of benefits, comes into play.
It’s a digital two-way radio system that uses digital rather than analog transmission to send and receive data and voice. Till the end of 20th century, radios were mostly used for transmitting and receiving non-digital or analogue voice signals and for remote control switching actions.
As 2024 progresses, let’s take a closer look at DMR, its importance, and how popular this technology has recently become.


Analog Radio vs DMR Comparison: What Are the Benefits?
While two-way communication has always been accomplished by analog radio. Lets understand the concept of conventional Analogue radio first. Analog radio communication refers to the traditional method of transmitting and receiving audio signals over radio frequencies using analog technology. In this system, voice or audio information is converted into electrical signals that vary continuously in amplitude or frequency. These signals are then transmitted through the air via radio waves. A receiving device, kept at a far distance without any physical contact with the transmitter, converts back these signals into audible sound.
Here the signal is continuously varying, which can result in potential drawbacks such as susceptibility to interference, static, and noise. These factors can sometimes affect the clarity and quality of the transmitted audio. In case of higher frequency (HF) reliable communication is dependent on the atmospheric conditions and time.
This means that the signal is continuously varying, which can result in potential drawbacks such as susceptibility to interference, static, and noise. These factors can sometimes affect the clarity and quality of the transmitted audio.
Analog radio systems have been used for decades in various applications, including broadcasting, public safety, aviation, maritime communication, and personal two-way radios. While they have served reliably for many years, analog systems are gradually being replaced by Digital Radio.
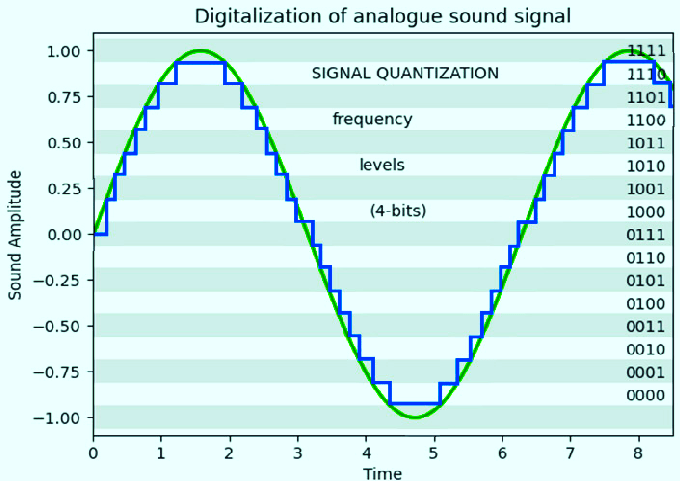
Everything here is similar, except the major the fundamental being, this communication utilizes by encoding audio signals into binary data i.e., into 0’s and 1’s, hence converting the analog signal into a digital format through sampling and quantization which in simple terms is the process of mapping continuous infinite values to a smaller set of discrete finite values.
A major difference in both technology is that DMR utilizes networks like the internet hand in hand in sync with direct simplex air waves.
DMR has a number of noteworthy benefits
Better Quality: As previously indicated, the digital nature of DMR results in audio that is crisper and less static and background noise, making it easier to understand, particularly in emergency situations.
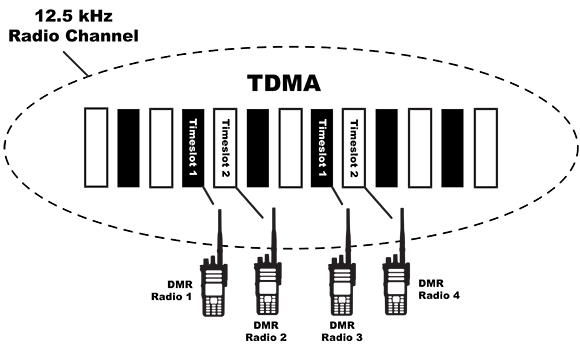
Increased Support: Supports a lot more users on a single channel because of TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access: digital modulation technique used in digital mobile technology). For large teams or companies in particular, this results to better resource utilization and increased communication efficiency.
Enhanced security: DMR provides an additional degree of protection for sensitive communication by offering optional encryption capabilities.
Data capabilities: DMR may send data packets in addition to voice messages, enabling features like text messaging, GPS position sharing, and status updates. The effectiveness of communication as a whole is improved by this increased data capabilities.
Cost-effectiveness: Although DMR equipment may initially cost a little more than analog, the enhanced functionality, larger capacity, and lower maintenance costs of digital technology can result in long-term cost benefits.


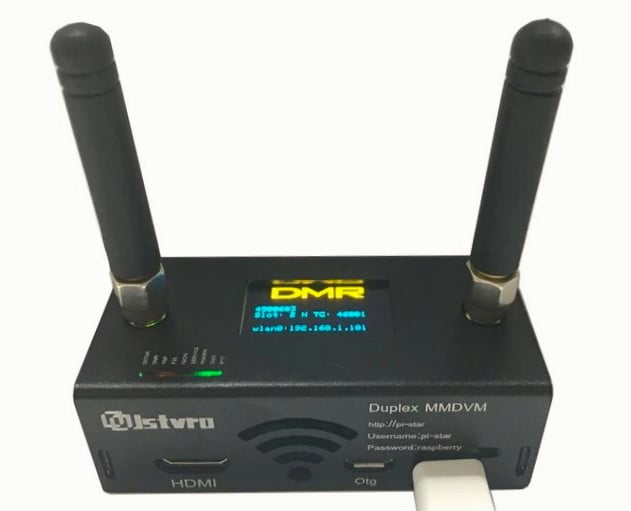
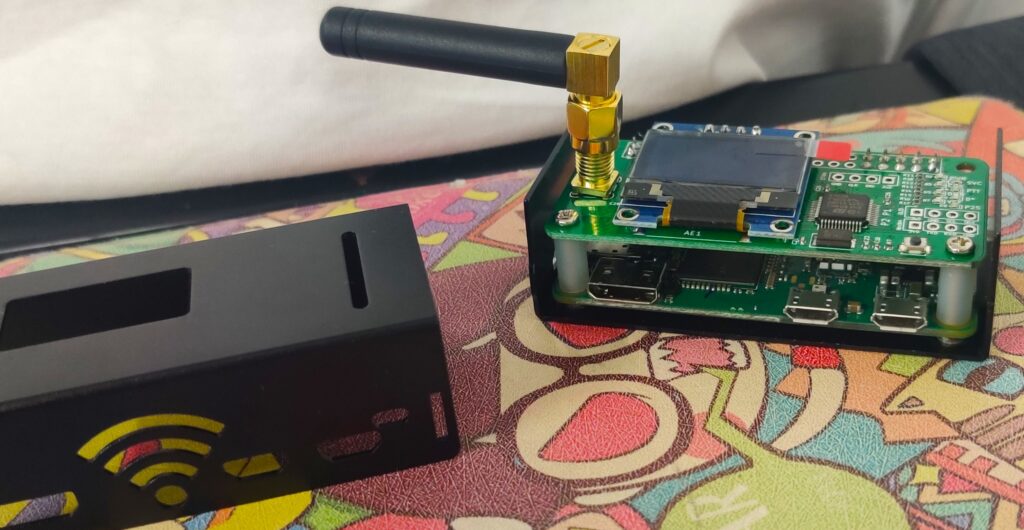
What is a Hotspot?
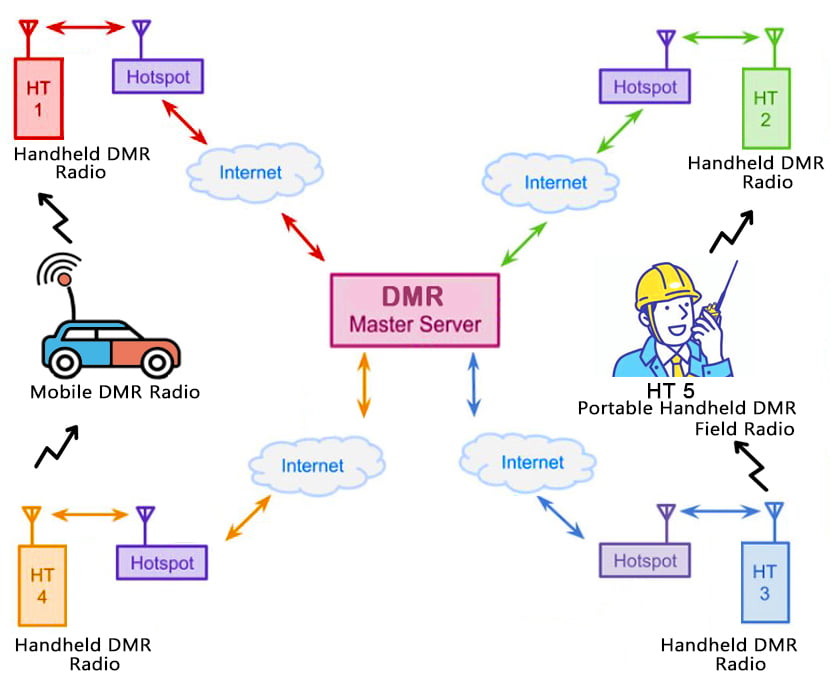
DMR users communicate with each other globally through repeaters or DMR “hotspots”. A hotspot, simply put, is your internet gateway to a particular DMR network. Its a small device built around small Raspberry Pi single-board computer. Hotspots in DMR are similar to the cellular hotspots that most of us are already familiar with. Radio hotspots work the same way, if you lack repeater access (devices with high elevation antenna setup extending the operational range), you can use a hotspot to access a specific DMR network.
The hotspot is connected to the radio through VHF or UHF channels. Through LAN port or through wi-fi network the hotspot connects to the internet gateway.
Some Hotspots commonly used are: Zum Spot, Jumbo Spot, SharkRF Open Spot, MMDVM Hotspots etc.


Analyzing DMR’s Performance in 2024
As 2024 progresses, DMR will still become more popular and effective two-way radio technology used in a variety of sectors. Even though more modern two-way radio technologies like Cellular Direct Mode (CDM) and Long-Term Evolution (LTE) are already successful, DMR is anticipated to be around for the foreseeable future.
The following are some important elements influencing its ongoing success:
Encryption: DMR was primarily developed for civil and industrial applications the protection of the confidentiality of the exchanged information can be important. It offers several voice and data encryption protocols, like: ARC4 40 bit, DES 64 bit, AES128 128 bit & AES256 256 bit
Budget conscious: DMR provides a cost-effective mix between functionality, performance, and affordability, even though it isn’t the least expensive alternative. For a comparatively low cost, it offers substantial benefits over analog systems, which attracts enterprises on a tight budget.
Scalability: DMR systems may easily grow to meet changing needs because of their high scalability. The solution is future-proof because businesses and organizations may simply add more users or equipment as needed.
Wide usage: Due to its adaptability, DMR can be used in a wide range of situations. DMR serves a wide range of businesses’ communication needs, from public safety (police, fire departments, emergency services) and transportation (logistics, truckers, taxis) to manufacturing, construction, and hospitality. Not least to say, this is even being popularly used amongst Amateur Radio operators worldwide which is still an extremely popular hobby.
Instances of effectively executed DMR systems
Public safety: Due to DMR’s enhanced data capabilities, speech clarity, and dependability, many police departments and emergency services worldwide have switched to it, improving first responder coordination and safety.
Transportation and logistics: DMR is used by trucking businesses and logistics companies to keep drivers and dispatchers in clear contact, resulting in effective coordination and real-time information.
Hospitality: DMR is used by hotels and resorts to facilitate staff communication, enhance client service, and guarantee effective operations throughout sizable facilities.
Amateur Radio use: The use of DMR on amateur radio in the VHF and UHF channels started approximately in 2010. In 2014, the FCC formally authorized amateurs to use it. DMR Identification Numbers in amateur radio are assigned and maintained by RadioID Inc. DMR radios can display other Ham radio operator’s names, call signs, and locations by uploading their coordinated database to them.
What is a DMR Network?
The primary way to connect to a DMR Radio is via the DMR network, which can be visualized as a system of radios linked together using the internet. Its like the internet service provider operates its own independent network, allowing you to communicate with other ISPs as well as within its own network. This is similar to the concept of game consoles like Xbox and Playstation having standalone games, as well as the ability to play cross-platform multi-user games.
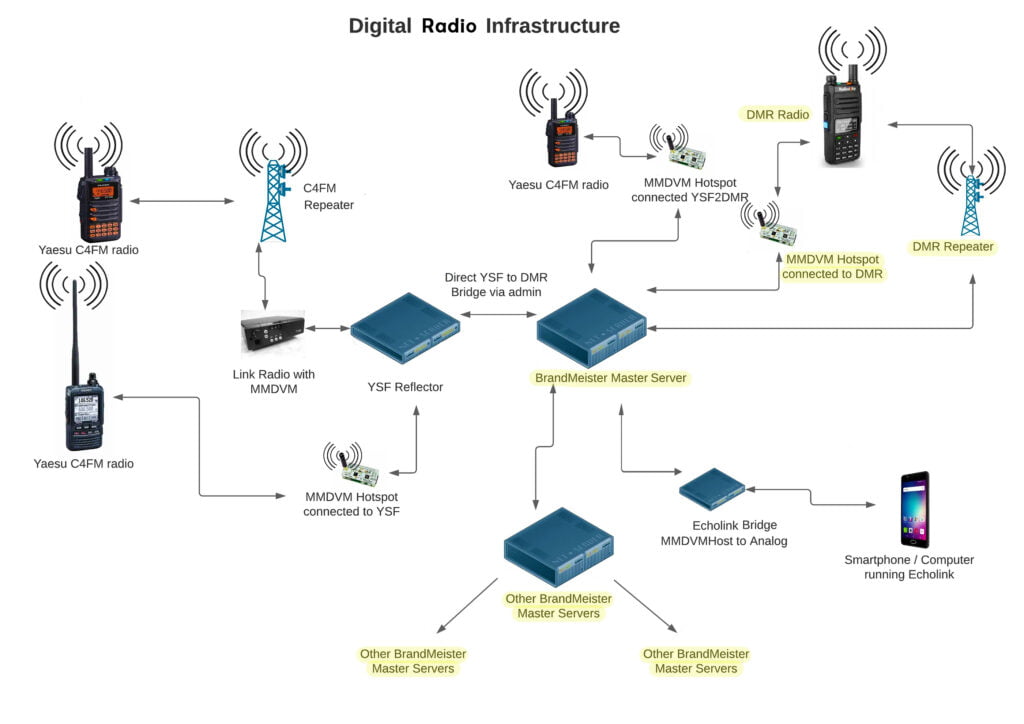
Repeaters and Hotspots communicate through a digital networking interface called TCP/IP, commonly associated with the internet. This interface transfers encoded information between two points, either privately or publicly. This includes the transmission of text, email, and GPS functionality.
Repeaters and hotspots utilize TCP/IP, the same digital networking interface used for internet connectivity, to communicate with each other. This interface enables the transfer of encoded data between two points, either privately or publicly, and supports various types of communication such as text, email, and GPS functionality. To transmit the encoded signal, DMR’s are equipped with an AMBE +2 Vocoder.
AMBE +2 Vocoder is nothing, but a DMR standard that transforms analog voice into a digital signal, allowing it to be transmitted with higher audio quality than traditional FM voice transmissions. This is achieved by encoding the analog voice into a digital signal that can be decoded by a radio with a matching digital signal.
Through internet-connected systems like the DMR-Marc, DMR+, BrandMeister, TGIF, FreeDMR, DV Scotland Phoenix Network, the UK’s Largest Digital Radio Network, and several others are now connected to larger networks for wide area accessibility. Presently, the BrandMeister system is connected to more than 5,500 repeaters and 16,000 “hotspots” across the globe, which one of the largest network of communication for HAM Radio operators.
Understanding DMR Standardization
Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) Tier I, II, and III make up the industry standard. Knowing how the DMR Tiers differ from one another helps the user choose the right radio system their needs.
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) established Digital Mobile Radio (DMR), an open digital mobile radio standard that is globally applicable. Users are not restricted to using proprietary solutions, and commercial products are required to adhere to it.
DMR employs a 12.5 kHz channel with two-slot TDMA, which gives you two communication slots as compared to one for analog transmission. This period is effectively divided into millisecond intervals, allowing for a doubling of capacity because users aren’t aware of the time gaps.
DMR Tier I: DMR products can be used in the European PMR446 band without a license. Products classified as Tier I are only intended for non-infrastructure use, which excludes the need for repeaters. With a maximum RF power of 0.5 watts, this section of the standard covers low-power commercial and consumer applications.
Because, there isn’t a license-free allocation at this frequency outside of Europe, PMR446 radios, including DMR Tier I devices, can only be used lawfully in other nations once the operator has the necessary radio license.
DMR Tier II: Mobiles, hand portables, and licensed conventional radio systems operating in PMR frequency ranges between 66 and 960 MHz are all covered under DMR Tier II. Users requiring integrated IP data services, sophisticated voice features, and spectral efficiency in licensed bands for high-power communications are the focus of Tier II standard.
DMR Tier III: Trunking operations in the 66–960 MHz frequency range are covered by tier. With built-in 128 character status messaging and up to 288 bits of data in a variety of forms for short messaging, Tier III enables voice and short messaging handling.
Do You Need a License for DMR Radio?
To operate a DMR radio, you may require a license depending on a number of criteria, such as:
Where are you based?: Countries and even areas within a country have quite different licensing requirements for two-way radio transmission.
What frequency are you using?: DMR can function on a range of frequencies, some of which may need a license to use, while others may not for certain purposes.
The reason you are using it: There may be different licensing requirements for using a DMR radio for personal or recreational use than for commercial or business use.
As a general rule of thumb, to transmit over DMR frequencies, a license is typically required. Usually, a government organization in charge of managing and allocating radio spectrum issues this license.
Generally, using DMR frequencies for listening (receiving) is permitted without a license. However, depending on the frequency spectrum and where you live, some rules can be applicable.
Amateur Nostalgia: The fear of Digitalization
For the Amateur Radio operators, operating wireless is more of a direct thing, i.e. use of radio without the help of any other man-made electronic network. They still cherish more, its ease of use, line of sight communication, and affordable price make it a good choice for casual, short-range, or long range contacts, though enjoying the statics (radio cracklings) and occasional blackouts, making enjoyable communication scenarios with inadequate infrastructure.
For all amateurs around the world, the hobby is all about tinkering with electronic radio circuits and antenna with available resources. Many do have the digital-phobia, and still try to cling to the conventional analogue ways, rejecting the digitally evolved toys.
Well, many would say that its a luddite old school thought, but to some extent its true. But with this continuing perception, we cannot stop encouraging the development and evolution of different modern modes of interconnectivity in communication technologies. So, gradual adaptability is the key to success.
Coexistence : The Key to Success
DMR serves customers who need more sophisticated functionality with a worldwide coverage, but syncing the analogue mode with the prior still is very much helpful for many real-time applications or for backup communication.
We should not forget that the birth of DMR has been only possible due to the age old analogue radio and internet technology
DMR’s effect on direct simplex communication will ultimately depend on a number of variables, including user acceptance rates, technical developments, and personal communication requirements. After all with DMR the users do not need to depend on terrain and atmospheric hinderances for a reliable contact. Both have a definitive role in the worlds transmission technologies, and depending on the situation and the user’s choices, how they are used may evolve and change in future.
WATCH THIS VIDEO ABOUT THE LATEST DIGITAL RADIO FROM MOTOLROLA






