Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Path to Immersive Opportunities
In a world where screens and text messages are taking over, communication’s future seems clouded by digital mist. However, what if technology could transcend flat interfaces and take us to fully immersive environments? Today technology has unlocked the potential of virtual reality to transform society. Enter the exciting world of VR glasses, poised to revolutionize the way we connect, share, and understand each other.
Will VR glasses be used for all audio visual entertainment and communication in the future? Although there is no easy yes or no response, the potential is clear. Let’s investigate popular terminologies, and look at successful products that are already influencing this developing subject, and assess the state of the industry now, briefly pointwise.


The Rise of Virtual Reality Gear
VR glasses, also known as virtual reality headsets or goggles, have witnessed a fleeting rise in popularity in the recent years. These devices immerse users in a simulated environment, enabling them to interact with digital content in a highly immersive and perceptible manner. From gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare, VR glasses are being integrated into diverse fields, revolutionizing how we communicate and engage with one another.
Trends Driving VR Headsets Adoption: Several key trends are driving the widespread acceptance
- Enhanced Immersive Experiences: VR glasses offer unparalleled sensations, transporting users to virtual worlds where they can experience sights, sounds, and interactions in a way that feels incredibly real.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in display technology, graphics rendering, and motion tracking have significantly improved the quality and realism of VR experiences, making them more compelling and lifelike.
- Diverse Applications: VR gadgets are finding applications across various industries, including gaming, entertainment, education, training, healthcare, and remote collaboration, showcasing their versatility and potential to revolutionize communication.
- Growing Accessibility: VR glasses are becoming more affordable and available to consumers, thanks to advancements in manufacturing processes and the introduction of standalone devices that eliminate the need for expensive gaming PCs or consoles.


Popular Terminology associated
- Metaverse: A persistent, shared virtual world accessed through devices like VR glasses, where users can interact, create, and socialize. Think of it as the next evolution of the internet in a much wider spectrum, with a 3D spatial dimension.
- Telepresence: The feeling of being physically present in a virtual space, even when geographically distant, possibly everywhere. This enables remote collaboration and communication that feels natural.
- Empathy building: VR experiences settle users in different perspectives, nurturing understanding and compassion for other’s.


- Virtual collaboration: VR tools are transforming how teams work together, allowing for real-time design reviews, brainstorming sessions, and even virtual training simulations regardless of their location.
- Gamification of learning: It is an approach to education that incorporates elements of game design into the learning process. The key idea is to make learning more enjoyable and interactive, ultimately leading to better knowledge retention and motivation for students.
- Augmented Reality: AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enriching your surroundings. Imagine directions popping up on your phone screen as you walk, or trying on virtual clothes before buying them. It enhances your physical environment instead of replacing it, offering a blend of digital and real experiences.


- Mixed Reality: MR blends real and virtual worlds, allowing users to interact with digital objects within their physical environment. It offers a unique layer of immersion compared to VR, where users are completely transported to a virtual space.
- Decentralized VR: This emerging trend envisions a VR ecosystem built on blockchain technology, where users own their data and virtual assets, independent of centralized platforms.
- Haptic feedback: People using smartphones are familiar with this. The technology that provides physical sensations through the hardware touching the user body through pulses and physical vibrations, enhancing sensory realism. Imagine feeling the texture of virtual objects or the impact of virtual interactions.
- Spatial computing: This refers to the interaction between digital information and the physical world, often using AR (Augmented Reality) and VR technology. Imagine manipulating 3D objects in real-time using hand gestures or other natural interactions. It’s about bridging the gap between screens and physical spaces, creating new possibilities for learning, working, and entertainment.


VR Companies and Devices in the Lead
Apple: The much awaited Apple Vision Pro, with mixed reality (MR) features and an emphasis on creativity, productivity, and entertainment, has been launched in February 2024. It’s already creating a lot of talk and may change the VR game altogether with its plethora of features. Its comes with the huge price tag out of all others in the market, except Microsoft’s VR gears.
Meta: Their Quest 3 headset is a popular choice for gaming and social VR experiences, like the “Horizon Worlds”. Zuckerberg claims his Quest3 is far better than the newly launched Apple Vision Pro.
HTC: Designed for professional applications, the Vive XR Elite of 2023 boasts precise tracking and high-resolution images. Its for users seeking a premium experience with both standalone and PC VR capabilities. Its lightweight design, high-resolution display, and accurate tracking make it a compelling option amongst others.
Valve: The Index VR Kit appeals to tech-savvy fans with its high-end technology and its video game digital distribution service ,Steam VR integration. Its optimized screen pixel layout, high frame rate and innovative off-the-ear audio hardware claim to provide superior immersion and comfort.


Sony: By utilizing Sony’s well-established gaming ecosystem, the PlayStation VR headset closes the gap between gaming and VR experiences. Its incredible 3D audio and built-in mic claims to provides ultra-realistic gaming performance.
Microsoft: Users may interact with holographic information in the real world with its pricy mixed reality headgear, the HoloLens 2, which focuses on enterprise solutions. Its an untethered self-contained holographic device to increase user accuracy and output. It offers off-the-shelf applications and build custom solution using Microsoft Azure services
HP: With its high-resolution displays and cozy design, the HP Reverb G2, developed in collaboration with Valve and Microsoft, provides a more cost-effective virtual reality experience, making it a well-liked option for both individuals and enterprises.
VR Communication Examples in Action
Virtual meetings: Envision working remotely with colleagues or going to a conference while feeling as though you are in the same room. This is becoming a reality thanks to platforms like Spatial and VR Chat.
Long-distance relationships: By allowing couples to explore virtual worlds together, virtual reality experiences like Waltz of the Wizard help them stay connected even when they are physically apart.
Empathy training: By placing users in the shoes of others, virtual reality simulations can encourage compassion and empathy in fields like education and healthcare. Imagine VR to study historical events, dissect a virtual frog in biology class, or practice surgery in a risk-free setting. VR is increasing the effectiveness and immersion of learning.
Enhanced Gaming engagement: VR makes you an active participant in the game, not just a passive observer. Your physical movements, voice, and even emotions can influence the game world, creating a deeper level of connection.
Viewing Entertainment: It engrosses yourself in documentaries, concerts, sporting events, and live shows as if you were actually there. This puts you right in the heart of the action, offering unparalleled TV and Cinema viewing experiences
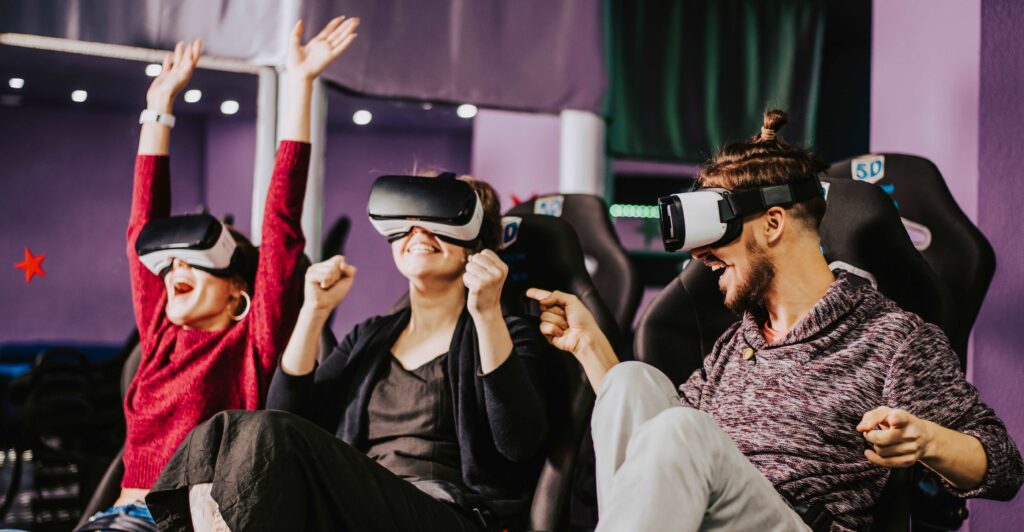
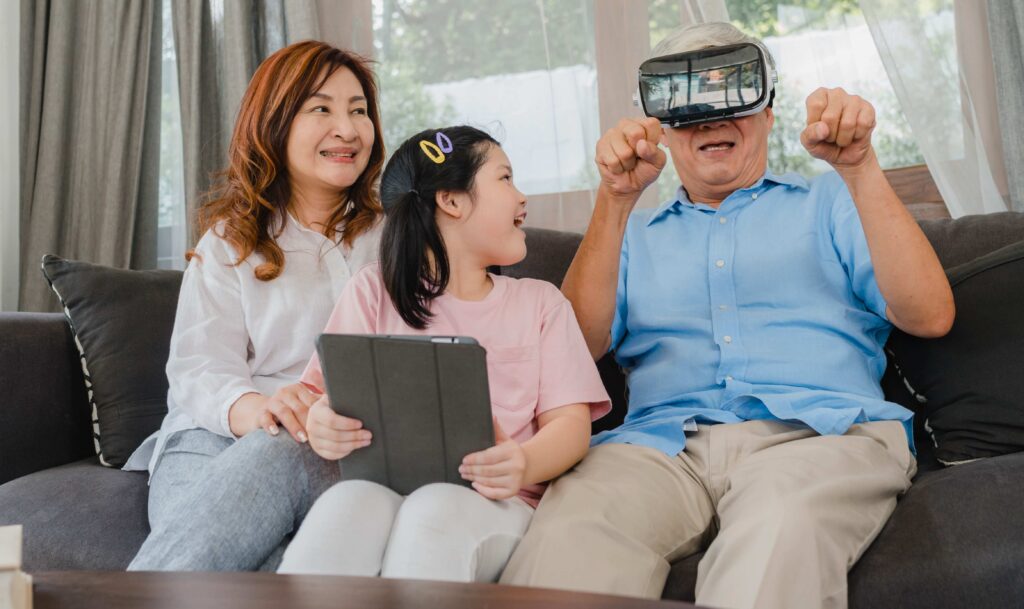


Challenges and Things to Think About
But, other than all the Potential Benefits discussed, Virtual reality has some obstacles, despite the tremendous prospects. It been taking lot of backlashes from the Luddite society.
Cost: The high price of high-end VR headsets may restrict its accessibility for the average person.
Content: The creation of compelling virtual reality experiences continues, necessitating ongoing funding and research-development.
Technical restrictions: Current VR technology with bulky gear can be quite uncomfortable, hindering long-term use.
Ethical considerations: Finally, data privacy and security risks associated with VR platforms collecting user information require robust safeguards to prevent misuse and potential manipulation.
Health concerns of Virtual Reality Headsets
While the immersive potential of the technology is undeniable, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential health hazards before fully enticing them. One major concern is cybersickness, triggered by the mismatch between visual and vestibular balance inputs. Studies show up to 70% of users experiencing nausea, dizziness, and headaches, potentially leading to aversion and limiting use. Additionally, it can induce visual discomfort, with prolonged exposure potentially impacting eye strain, convergence issues, and even contributing to myopia development in children, as seen in a recent study by Leeds University.
Furthermore, the immersive nature of VR raises concerns about psychological impacts. Cases of anxiety, panic attacks, and disillusionment have been reported, particularly in users with pre-existing mental health conditions. Additionally, the potential for addiction to the hyper-stimulating environment, neglecting real-world responsibilities, needs careful consideration.
Remember, it’s important to consult with medical professionals before engaging in VR experiences, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions. Additionally, responsible usage practices like taking breaks, ensuring proper ventilation, and limiting session lengths can help mitigate potential risks.
Conclusion
In spite of these obstacles, this field appears to have a promising future in the 21st century mobile digital gadgetry scenario, provided we use it cautiously, by not overstraining our sensory perceptions or getting totally detached from the real world. With the phenomenal advent of AI in this century, and hardware ameliorations, VR is positioned to become a commonplace medium for communication as costs fall down with time, technology progresses, and content development soars.
Virtual reality headsets are a powerful tool that have the potential to completely change the way we interact, communicate, and learn, even though they may not be the only way communication develops in the future. It has the potential to significantly influence how people communicate in the future as technology advances.